rizer.io.thermo_transport_data_reader#
Attributes#
Classes#
Load and process the thermodynamic and transport data for a gas, assuming LTE. |
Module Contents#
- class rizer.io.thermo_transport_data_reader.ThermoTransportDataReader(gas_name: str, pressure_atm: int, source: str, skip_missing_values: bool = False)#
Load and process the thermodynamic and transport data for a gas, assuming LTE.
LTE (Local Thermodynamic Equilibrium) means that thermal and chemical equilibrium are established. The data is assumed to be given at a fixed pressure.
Methods are provided to interpolate the data and plot it. The interpolations are linear, and out-of-bounds values take the value at the boundary.
- Parameters:
gas_name (
str) – Gas used for the thermo/transport data.pressure_atm (
int) – Pressure (in atm) for the thermo/transport data.source (
str) – Source used for the thermo/transport data.skip_missing_values (
bool, optional) – Whether to skip missing values in the data file (default is False).
Examples
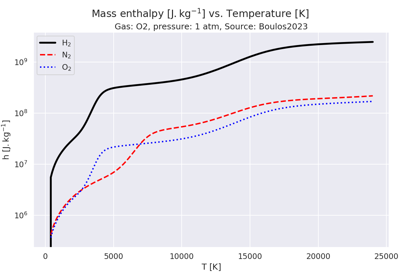
Plot thermo data vs. temperature for a plasma of H2, O2 or N2 in LTE.
Plot thermo data vs. temperature for a plasma of H2, O2 or N2 in LTE.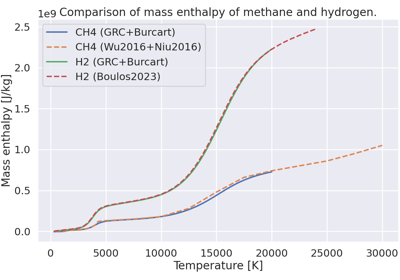
Plot mass enthalpy vs. temperature for methane and hydrogen.
Plot mass enthalpy vs. temperature for methane and hydrogen.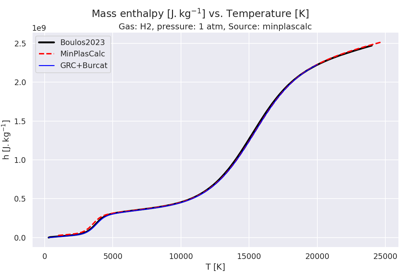
Plot thermodynamic properties of H₂ vs. temperatures.
Plot thermodynamic properties of H₂ vs. temperatures.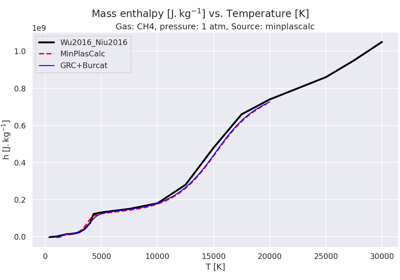
Plot thermodynamic properties of CH₄ vs. temperatures.
Plot thermodynamic properties of CH₄ vs. temperatures.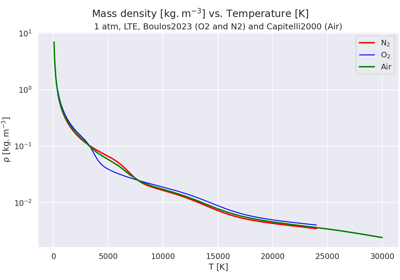
Plot thermodynamic and transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of Air, O2 or N2 in LTE.
Plot thermodynamic and transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of Air, O2 or N2 in LTE.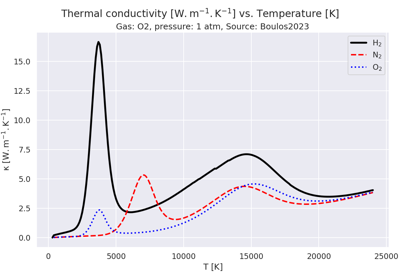
Plot thermodynamic and transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of H2, O2, N2, Ar, He in LTE.
Plot thermodynamic and transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of H2, O2, N2, Ar, He in LTE.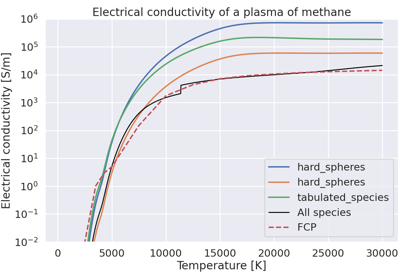
Plot electrical conductivity vs. temperature for a plasma of methane.
Plot electrical conductivity vs. temperature for a plasma of methane.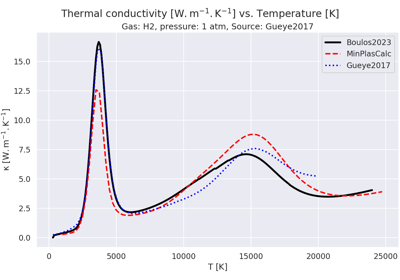
Plot transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of hydrogen.
Plot transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of hydrogen.
Plot transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of methane.
Plot transport data vs. temperature for a plasma of methane.- skip_missing_values = False#
- temperature#
- density#
- enthalpy#
- heat_capacity_constant_pressure#
- dynamic_viscosity#
- thermal_conductivity#
- electrical_conductivity#
- theta#
- load_data() tuple[numpy.ndarray, Ellipsis]#
Load the data from the files.
Files are expected to be in ./data/transport.
The thermo/transport data file is expected to be a CSV file with the following columns:
Temperature [K]
Density [kg/m3]
Enthalpy [J/kg]
Specific heat [J/kg.K]
Viscosity [kg/m.s]
Thermal conductivity [W/m.K]
Electrical conductivity [S/m]
It is assumed that the data is sorted by increasing temperature. It is also assumed that the header is 3 lines long.
- Returns:
Tuple containing the following arrays:
temperature: Temperature [K]
density: Density [kg/m3]
enthalpy: Enthalpy [J/kg]
cp: Specific heat at constant pressure [J/kg.K]
dynamic_viscosity: Viscosity [kg/m.s]
thermal_conductivity: Thermal conductivity [W/m.K]
electrical_conductivity: Electrical conductivity [S/m]
- Return type:
tuple[np.ndarray,]
- compute_theta() numpy.ndarray#
Compute the integrated thermal conductivity.
Notes
The integrated thermal conductivity is defined as:
\[\theta = \int_0^{T} \kappa(T') dT'\]It is computed using the trapezoidal rule.
- rho(T: float) float#
Get the density at a given temperature.
- Parameters:
T (
float) – Temperature [K].- Returns:
Density [kg/m^3] at the given temperature.
- Return type:
float
- h(T: float) float#
Get the enthalpy at a given temperature.
- Parameters:
T (
float) – Temperature [K].- Returns:
Enthalpy [J/kg] at the given temperature.
- Return type:
float
- T_from_h(h: float) float#
Get the temperature at a given enthalpy.
- Parameters:
h (
float) – Enthalpy [J/kg].- Returns:
Temperature [K] at the given enthalpy.
- Return type:
float
- cp(T: float) float#
Get the heat capacity at constant pressure at a given temperature.
- Parameters:
T (
float) – Temperature [K].- Returns:
Heat capacity at constant pressure [J/(kg.K)] at the given temperature.
- Return type:
float
- mu(T: float) float#
Get the dynamic viscosity at a given temperature.
- Parameters:
T (
float) – Temperature [K].- Returns:
Dynamic viscosity [kg/(m.s)] at the given temperature.
- Return type:
float
- kappa(T: float) float#
Get the thermal conductivity at a given temperature.
- Parameters:
T (
float) – Temperature [K].- Returns:
Thermal conductivity [W/(m.K)] at the given temperature.
- Return type:
float
- sigma(T: float) float#
Get the electrical conductivity at a given temperature.
- Parameters:
T (
float) – Temperature [K].- Returns:
Electrical conductivity [S/m] at the given temperature.
- Return type:
float
- plot(x: str, y: str, show: bool = True, yscale: str = 'linear', fig_ax: tuple[matplotlib.figure.Figure, matplotlib.axes.Axes] | None = None, ax_title: str | None = None, **plot_options) tuple[matplotlib.figure.Figure, matplotlib.axes.Axes]#
Plot data.
- Parameters:
x (
str) –The variable to plot on the x-axis. Options are:
”temperature” or “T”: Temperature in Kelvin.
”theta”: Integrated thermal conductivity in W/m.
y (
str) –The variable to plot on the y-axis. Options are:
”temperature” or “T”: Temperature in Kelvin.
”enthalpy” or “h”: Enthalpy in J/kg.
”density” or “rho”: Density in kg/m³.
”heat_capacity” or “c_p”: Heat capacity at constant pressure in J/(kg·K).
”dynamic_viscosity” or “mu”: Dynamic viscosity in Pa·s.
”electrical_conductivity” or “sigma”: Electrical conductivity in S/m.
”thermal_conductivity” or “kappa”: Thermal conductivity in W/(m·K).
”theta”: Integrated thermal conductivity in W/m.
show (
bool, optional) – Whether to display the plot immediately (default is True).yscale (
str, optional) – The scale of the y-axis. Options are “linear” or “log” (default is “linear”).fig_ax (
tuple[Figure,Axes] | None, optional) – A tuple containing a Matplotlib Figure and Axes to plot on. If None, a new figure and axes are created (default is None).**plot_options – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the plotting function. E.g., label, color, linestyle, marker, etc.
- Returns:
The figure and axes objects of the plot.
- Return type:
tuple[matplotlib.figure.Figure,matplotlib.axes.Axes]- Raises:
ValueError – If an invalid variable is specified for the x or y axis.
Examples
>>> from rizer.io.thermo_transport_data_reader import ThermoTransportDataReader >>> # Define the hydrogen data. >>> hydrogen_data = ThermoTransportDataReader( ... gas_name="H2", ... pressure_atm=1, ... source="Boulos2023", ... ) >>> # Plot the data. >>> hydrogen_data.plot(x="temperature", y="enthalpy")
- plot_all(x: str = 'temperature', show: bool = True, yscale: str = 'linear', fig_ax: tuple[matplotlib.figure.Figure, matplotlib.axes.Axes] | None = None, **plot_options)#
Plot all data.
See
plot()for parameters.
- rizer.io.thermo_transport_data_reader.CH4_lte_data_minplascalc#
